Modeling population accessibility to health facilities has always been tedious and time-consuming. From the selection of relevant data sources to the modeling in itself, a wide range of skills and software solutions are required. GeoHealthAccess is a tool that aims to automate the process using a set of high resolution, global and open datasets -- in order to enable fast and automated country-scaled analysis. To that end, input datasets are automatically pulled from various sources:
- Geofabrik (OpenStreetMap) for the transport network ;
- Copernicus Global Land Cover for land cover ;
- Global Surface Water for surface water ;
- Shuttle Radar Topography Mission for topography ;
- and WorldPop for population maps.
GeoHealthAccess have three system dependencies: gdal is used to process raster data, osmium-tool to process
OpenStreetMap data and grass to perform a cost distance analysis. Alternatively, a docker image is also available (see
below).
# Ubuntu 20.04
apt-get install gdal-bin osmium-tool grass-coreThe python package can then be installed using pip:
# Download source code
git clone https://github.com/BLSQ/geohealthaccess
cd geohealthaccess
pip install -e .
# To install devevelopment dependencies such as pytest, use:
pip install -e .[dev]The geohealthaccess program is divided into three commands:
downloadfor automatic data acquisitionpreprocessfor preprocessing of input dataaccessto compute travel times
geohealthaccess --helpUsage: geohealthaccess [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Map accessibility to health services.
Options:
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
access Map travel times to the provided health facilities.
download Download input datasets.
preprocess Preprocess and co-register input datasets.
NASA EarthData credentials are required to download SRTM tiles. An account can be created here.
geohealthaccess download --helpUsage: geohealthaccess download [OPTIONS]
Download input datasets.
Options:
-c, --country TEXT ISO A3 country code [required]
-o, --output-dir PATH Output directory
-u, --earthdata-user TEXT NASA EarthData username [required]
-p, --earthdata-pass TEXT NASA EarthData password [required]
-f, --overwrite Overwrite existing files
--help Show this message and exit.
If output-dir is not provided, files will be written to ./data/raw.
NASA EarthData credentials can also be set using environment variables:
export EARTHDATA_USERNAME=<your_username>
export EARTHDATA_PASSWORD=<your_password>geohealthaccess preprocess --helpUsage: geohealthaccess preprocess [OPTIONS]
Preprocess and co-register input datasets.
Options:
-c, --country TEXT ISO A3 country code [required]
-s, --crs TEXT CRS as a PROJ4 string [required]
-r, --resolution FLOAT Pixel size in `crs` units
-i, --input-dir PATH Input data directory
-o, --output-dir PATH Output data directory
-f, --overwrite Overwrite existing files
--help Show this message and exit.
If not specified, input-dir will be set to ./data/raw and output-dir to ./data/input.
geohealthaccess access --helpUsage: geohealthaccess access [OPTIONS]
Map travel times to the provided health facilities.
Options:
-i, --input-dir PATH Input data directory
-o, --output-dir PATH Output data directory
--car / --no-car Enable/disable car scenario
--walk / --no-walk Enable/disable walk scenario
--bike / --no-bike Enable/disable bike scenario
-s, --travel-speeds PATH JSON file with custom travel speeds
-d, --destinations PATH Destination points (GeoJSON or Geopackage)
-f, --overwrite Overwrite existing files
--help Show this message and exit.
If not specified, input-dir is set to ./data/input, interm-dir to
./data/intermediary and output-dir to ./data/output. By default, only the
car scenario is enabled and if no destinations are provided, health facilities extracted from OpenStreetMap will be
used as target points for the cost distance analysis. Likewise, default values for travel speeds are used if
the --travel-speeds option is not set.
Three output rasters are created for each enabled scenario and provided destination points:
cost_<scenario>_<destinations>.tif: cumulated cost (or travel time, in minutes) to reach the nearestdestinationsfeature.nearest_<scenario>_<destinations>.tif: ID of the nearestdestinationsfeature.- and
backlink_<scenario>_<destinations>.tif: backlink raster.
Directories and files provided as option to the geohalthaccess CLIs can be located on S3 and GCS buckets. Paths must be
prefixed with s3:// or gcs://, for instance:
geohealthaccess download \
--country BDI \
--output-dir "s3://<bucket_name>/bdi/data/raw" \
--logs-dir "s3://<bucket_name>/bdi/logs"
geohealthaccess preprocess \
--country BDI \
--crs "EPSG:3857" \
--resolution 100 \
--input-dir "s3://<bucket_name>/bdi/data/raw" \
--output-dir "s3://<bucket_name>/bdi/data/input" \
--logs-dir "s3://<bucket_name>/bdi/logs"
geohealthaccess acces --car --no-walk --no-bike \
--input-dir "s3://<bucket_name>/bdi/data/input" \
--interm-dir "s3://<bucket_name>/bdi/data/intermediary" \
--output-dir "s3://<bucket_name>/bdi/data/output" \
--logs-dir "s3://<bucket_name>/bdi/data/logs"The following environment variables are required to allow S3 and/or GCS access:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_REGION(defaults tous-east-1)S3_ENDPOINT_URLGOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS(path to JSON file containing credentials)
Creating a map of travel times to the nearest health facility for Burundi:
# Download input datasets
geohealthaccess download \
--country BDI \
--earthdata-user <your_username> \
--earthdata-pass <your_password>
# Preprocess input datasets to a common raster grid
geohealthaccess preprocess \
--country BDI \
--crs "EPSG:3857" \
--resolution 100
# Compute travel times to nearest health facility for the `car` and `walk`
# scenarios.
geohealthaccess access --car --walk
# Or use your own data for destinations:
geohealthaccess access --car --walk -d hospitals.geojson -d clinics.geojsonA docker image is available on Docker Hub. To launch the
geohealthaccess app locally:
cd <path_to_geohealthaccess>
docker run -v $(pwd):/project:rw blsq/geohealthaccess:latestWe also provide a docker-compose.yml file to facilitate local development using Docker:
cd <path_to_geohealthaccess>
docker-compose build
docker-compose run appImages are automatically rebuilt and published on Docker Hub through a GitHub workflow triggered each time a new release is published in this repo. Alternatively, you can also trigger the workflow manually from the Actions section.
We use pytest for our test suite. Make sure that the development dependencies are installed, and simply launch the
test command using the CLI (or using Docker: docker-compose run app test).
The whole flow (download, preprocess and access) can be orchestrated using
Apache Airflow. The DAG can be found in the airflow directory and is ready to used.
It relies on a few Airflow variables to run:
gha_earthdata_usernameandgha_earthdata_passwordfor the EarthData credentialsgha_aws_access_key_id,gha_aws_secret_access_keyandgha_aws_regionfor AWS S3 storage if appropriategha_google_application_credentialsfor GCP GCS storage if appropriate
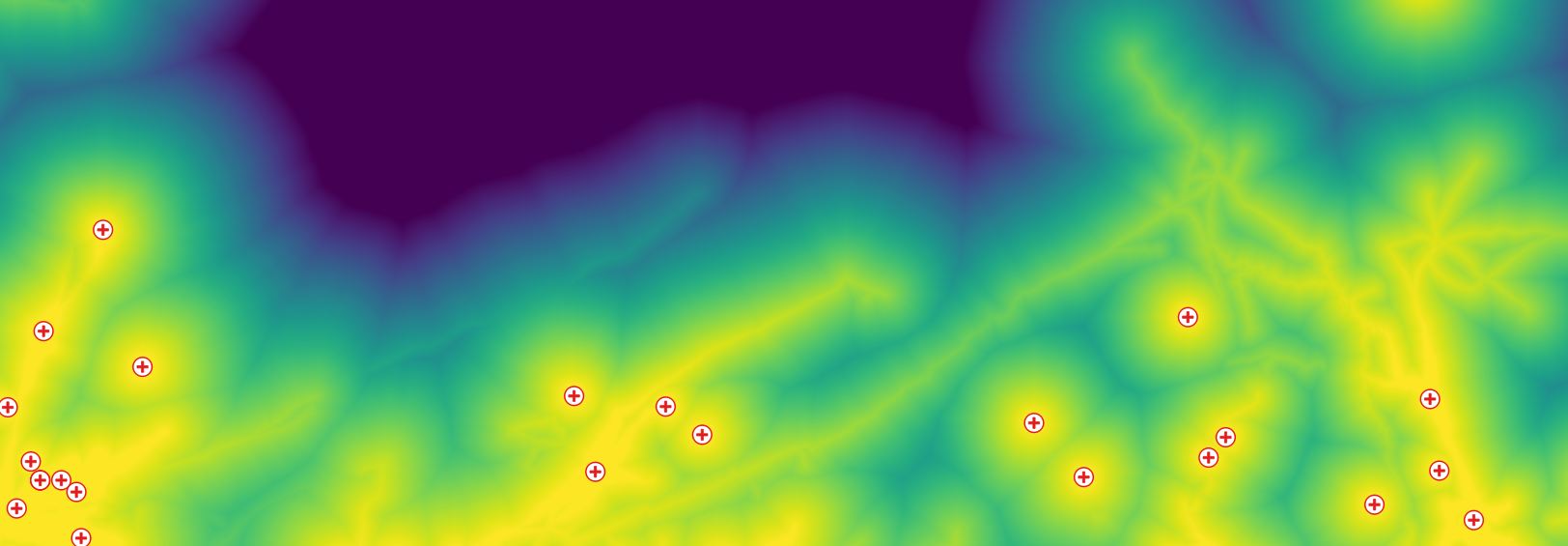
 : Processing chain (red=input, yellow=intermediary, green=output).
: Processing chain (red=input, yellow=intermediary, green=output).
The GeoHealthAccess project is funded by Innoviris and led by a partnership between Bluesquare and the Spatial Epidemiology Lab (Université Libre de Bruxelles). The project is based on a previous work from IGEAT-ANAGEO (Université Libre de Bruxelles) and the Department of Geography (University of Namur) in the She Decides project.
- Grégoire Lurton (Bluesquare)
- Yann Forget (Spatial Epidemiology Lab, Université Libre de Bruxelles)
- Moritz Lennert (IGEAT-ANAGEO, Université Libre de Bruxelles)
- Sabine Vanhuysse (IGEAT-ANAGEO, Université Libre de Bruxelles)
- Taïs Grippa (IGEAT-ANAGEO, Université Libre de Bruxelles)
- Catherine Linard (Department of Geography, University of Namur)
- Pierre Vanliefland (Bluesquare)